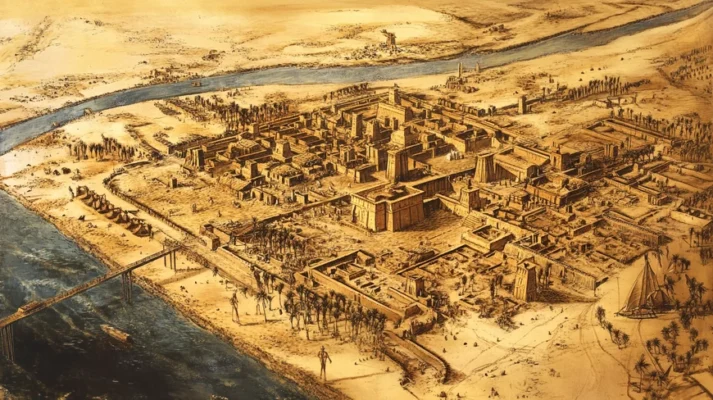
Bubastis was one of the largest and most important cities of ancient Egypt, located in the Nile Delta, in the northern part of the country. The city became famous for its huge temple to the goddess Bastet, who was the goddess of fertility, cats, and women. Bubastis was an important religious center, and pilgrims came from all over the country to pay homage to Bastet.
The city has existed since the Ancient Kingdom, but gained its greatest fame and importance during the XXII Dynasty (ca. 950-720 BC). Every year, Bubastis hosted grand festivities in honor of Bastet, which lasted several days and included musical performances, dances, and religious rites.
Archaeological excavations of Bubastis have revealed numerous artifacts that testify to the high level of development of culture and religion in this city. Nowadays, Bubastis remains an important research object, and its ruins are part of Egypt’s cultural heritage, attracting tourists and researchers from all over the world.
- Location and geography
- The role of Bubastis in Egyptian religion and culture
- Bastet Temple: significance and architecture
- The significance of the temple
- The architecture of the temple
- Bastet – the goddess of cats
- Myths and legends about Bastet
- Bubastis in Late Egyptian times
- The role of the city during the reign of different dynasties
- Archaeological excavations of Bubastis
- Bastet Temple: finds and reconstruction
- Bubastis’ legacy in the modern world
- Conclusion
Location and geography
Bubastis was located in northern Egypt, in the Nile Delta, west of the modern city of Port Said. The city was located on the Nile River, which provided it with convenient access to waterways and fertile land. This strategic location made Bubastis an important trade and religious center in ancient Egypt.
Bubastis was located in the northern part of Egypt, in the Nile Delta, about 75 km southwest of the modern city of Port Said. This place is located to the east of the modern canal connecting the Nile to the Mediterranean Sea, in an area that was strategically important due to its location on the waterways.
On the map of Egypt, Bubastis can be found in the central part of the delta, close to major cities such as Memphis and Tanis, which also had great cultural and religious significance in the ancient Egyptian era.
Due to its geographical location, Bubastis had favorable access to sea routes, which facilitated communication with other regions of Egypt and neighboring countries. The natural resources of the Nile Delta contributed to the development of agriculture and also contributed to the prosperity of the local economy.
Today, the site of Bubastis is an important archaeological site, and its ruins continue to attract the attention of researchers and tourists.
The role of Bubastis in Egyptian religion and culture
Bubastis played an important role in the religious and cultural life of Ancient Egypt due to its status as the main center of worship of the goddess Bastet, who was a symbol of fertility, love, motherhood, and the protector of domestic animals, particularly cats. The Temple of Bastet in Bubastis was one of the largest and most famous religious complexes in Egypt, and the city became a pilgrimage site for Egyptians seeking to worship the goddess and participate in festivities.
One of the most significant religious rituals was the celebration of the Bastet holiday, which was held annually. During the holiday, large-scale rituals were held in Bubastis, including songs, dances, musical performances, and large processions that attracted thousands of pilgrims from all over Egypt. This holiday became an important symbol of unity and national identity, as well as one of the most important religious events of the time.
In addition to its religious role, Bubastis was also of great cultural importance. The city was an important center for the development of Egyptian art, architecture, and literature. The huge Bastet temple, magnificent monuments and statues, as well as numerous wall reliefs depicting religious scenes and mythological subjects, testify to the high level of artistic development. Bubastis became a symbol of cultural heritage that influenced other Egyptian cities and regions.
Thus, Bubastis was not only a religious but also a cultural center that had a significant impact on the development of Egyptian civilization.
Bastet Temple: significance and architecture
The Temple of Bastet in Bubastis was one of the most magnificent religious complexes of Ancient Egypt, dedicated to the goddess Bastet, who was a symbol of fertility, motherhood, and the protector of cats. The temple was of great importance to the Egyptians as a center of worship, and the annual festival in honor of Bastet attracted thousands of pilgrims. This holiday was one of the most important events in the religious life of the country, which testifies to the greatness of the temple and its importance.
The significance of the temple
The Bastet temple was not only a religious but also a political symbol. This place became a symbol of Egyptian unity, as pilgrims from all over the country gathered here to participate in festivities, which strengthened ties between different parts of the country. The bastet was also associated with many important aspects of life: guarding the family, protecting against illness and misfortune, and maintaining well-being in the home.
The architecture of the temple
The architecture of the Bastet temple was majestic and grandiose, reflecting the importance of this religious complex. It consisted of numerous halls, courtyards, and sanctuaries where the main religious rituals were performed. The temple housed numerous statues and images of Bastet, including the famous statues in the form of cats or women with cat heads.
One of the most impressive elements of the temple architecture is the huge columns decorated with reliefs depicting scenes from Bastet’s life. The temple was surrounded by beautiful gardens and became an important cultural and spiritual center.
Due to its architectural splendor and significance, the temple of Bastet became one of the most famous religious sites in ancient Egypt, and even after the decline of Bubastis, its ruins remain a symbol of ancient Egyptian culture.
Bastet – the goddess of cats
Bastet is one of the most famous and revered goddesses of Ancient Egypt, associated with cats, fertility, motherhood, music, and the protection of the home. She was known by various names, including “Sukha” (protector), and her cult was popular throughout Egypt, but especially in Bubastis, where her main temple was located.
In mythology, Bastet represents maternal love and protection, as well as harmony and merriment. She is often depicted as a woman with a cat’s head or even completely in the form of a cat, emphasizing her close connection to these animals. Cats were sacred animals in Egypt, and their special role in everyday life gave Bastet another important aspect – protecting the household from pests.
Bastet also personified protection and was the patron saint of women and children, making her cult especially important to Egyptians who sought to ensure the well-being of their homes and families.
The cult of Bastet was one of the most widespread and important in ancient Egypt. Every year, Bubastis held large festivals in her honor, which attracted thousands of pilgrims from all over the country. During the celebrations, there were processions, dances, music and rituals that reflected joy and celebration. One of the symbols of Bastet was cats, which were often kept in the temple and even worshipped. Images of cats are often found on amulets, sculptures, and other objects that were supposed to protect people from evil spirits.
Thus, Bastet was not only the goddess of cats, but also an important symbol of protection, family well-being, and fertility, retaining its significance in the culture and religion of ancient Egypt for thousands of years.
Myths and legends about Bastet
Bastet, the goddess of cats and fertility, was associated with many myths and legends in ancient Egyptian mythology. Her cult and images were mixed with other deities, and the myths about Bastet evolved over the centuries, acquiring new features.
- The transformation of Bastet from a goddess of war to a goddess of peace One of the main myths is the transformation of Bastet from a goddess of war to a goddess of peace and fertility. Initially, Bastet was depicted as a warlike goddess, shaped like a lioness and symbolizing strength and aggression. She was associated with battles and defense. Later, however, her image changes and she becomes more peaceful, depicted as a soft and loving goddess who takes the form of a cat or a woman with a cat’s head. This change symbolized the transition from violence to the protection of the family hearth and harmony.
- The Legend of Bastet and Her Sons One popular legend connects Bastet with her son, a divine cat who was the embodiment of her powers. In one myth, Bastet gives birth to two sons: Sokara, the god of protection and fertility, and Mau, the god of cats, who acts as her patron. Bastet is often considered not only a protector, but also a mother who ensures the well-being of her home and family.
- Bastet and the god Ra In some myths, Bastet is mentioned as the daughter of the sun god Ra. Legend has it that Bastet was once on Ra’s side when he went to fight his enemies. Later, however, Bastet chose a softer path and became the protector of people from the evil forces that opposed Ra.
- The legend of revenge and forgiveness Another popular legend is related to Bastet and her vengeful nature. According to one myth, Bastet was sent to take revenge for her subjects who had been offended by evil forces. She became angry and aggressive, like a lioness, and waged war against her enemies. However, when she saw the destruction and pain her actions caused, Bastet repented and decided to return to her peaceful image, taking on the form of a cat, symbolizing calm and gentleness.
- Bastet and her cult Bastet was also an important figure in the cult of cats. According to myths, cats were sacred animals, and even killing them could be punishable by death. Legends say that Bastet protected cats and helped them protect their homes from pests and evil spirits. Cats were considered sacred animals, and they were often depicted in amulets, statuettes, and various religious objects.
These myths and legends about Bastet show her multifaceted image: from a warlike goddess to a peaceful patroness of the family, helping to maintain harmony and prosperity in the home.
Bubastis in Late Egyptian times
During the Late Egyptian period (mid 1st millennium BC – 4th century AD), Bubastis became one of the largest and most important religious and cultural centers of the country. This period was characterized by political and social instability, but it was during this time that the city gained new significance due to changes in government, religion, and cultural development.
- The role of Bubastis in Egyptian political life
During the late Egyptian period, when power was divided between different dynasties, Bubastis became an important city not only religiously but also politically. During the XXII Dynasty (ca. 950-720 BC), based in Bubastis, the city became one of the centers of political and administrative power. At this time, a new architectural foundation was laid, and the city gained even greater importance in the context of the Egyptian state system.
- Religious center
Bubastis was the main religious center for the worship of the goddess Bastet. The temple of Bastet that existed in the city was significant not only because of its size, but also because of the festivals held in honor of this goddess. In late Egyptian times, celebrations in honor of Bastet became widespread: every year thousands of pilgrims from all over Egypt came to Bubastis to participate in celebrations that included songs, dances, and religious rituals. This holiday became one of the largest religious events symbolizing the unity of Egypt.
- Economy and culture
During the late Egyptian period, Bubastis’ economy was closely linked to religious activities. The city flourished thanks to the flow of pilgrims and trade. Bubastis was an important center for crafts, artistic products, including the manufacture of statues, amulets, and religious objects related to the Bastet cult.
In addition, Bubastis had a significant cultural impact, as it was a center of Egyptian art, particularly in sculpture and architecture. Archaeological excavations have uncovered numerous reliefs, statues, and other artifacts that testify to the city’s high cultural activity.
- Heritage and decline
Over time, due to changes in the political situation, Bubastis gradually lost its importance. However, even during the period of decline, this religious center remained an important symbol of Egyptian culture and history. Excavations and research conducted at the site of Bubastis indicate that the city continued to exist long after its religious and cultural role had weakened.
Thus, Bubastis was an important religious, political, and cultural center in late Egypt, leaving a significant legacy that is still being studied by archaeologists and historians.
The role of the city during the reign of different dynasties
Bubastis, located in the Nile Delta, was an important cultural, religious, and political center at various stages of Ancient Egyptian history, including during the reigns of various dynasties. This city became one of the symbols of the Egyptian religion and state, and its role changed depending on the political situation in Egypt.
- Bubastis during the Ancient Kingdom (until 2181 BC)
During the Ancient Kingdom, Bubastis was not as well known and important as it was in later times. The city was just beginning to gain popularity due to its geographical location in the Nile Delta, which favored the development of agriculture and trade. However, although Bubastis was an important city, it was not yet a center of Bastet religious worship at the time, and its role at the national level was limited.
- Bubastis during the Middle Kingdom (2040-1640 BCE)
During the Middle Kingdom period, Bubastis began to gain greater importance as a religious and political center. This period is characterized by stability and the restoration of centralized power after the period of the “First Transition”. The city becomes an important commercial and administrative center. Although Bubastis was still not the main political center of the country, its importance as a religious and cultural center gradually increased.
- Bubastis during the New Kingdom (1550-1070 BC)
During the New Kingdom, Bubastis reached its greatest heyday. This happened during the reign of the XXII Dynasty (950-720 BC), when Bubastis became the main religious center of the country. The Bastet Temple, located in the city, was one of the largest and most famous in Egypt. The city became an important place of pilgrimage, and the annual festivals held in honor of Bastet attracted thousands of people from all over Egypt.
These festivals strengthened social and religious ties between different parts of the country. Bubastis became not only a religious but also a political symbol of Egyptian unity.
- Bubastis during the Late Egyptian period (1070-332 BC)
During the Late Egyptian period, especially during the reigns of the XXII and XXIII dynasties, Bubastis regained importance due to its cult status and role in administrative affairs. The city became the capital during the reigns of some pharaohs, notably during the reign of Sheshonk I, the founder of the XXII Dynasty.
During this time, Bubastis served as an important cultural and religious center, although the political situation was less stable. Bastet festivals continued to be an important part of Egyptian religious practice, and the city remained an important center for the development of arts and crafts.
- Bubastis after the conquest of Persia and Macedonia
After Egypt became part of the Persian Empire in the 6th century BC and later came under the rule of Alexander the Great (332 BC), the role of Bubastis changed. The city retained its importance as a religious center, but gradually lost its political weight. However, even during the periods of foreign conquest, Bubastis remained an important symbol of Egyptian culture and religion.
Bubastis changed its role in Egyptian history depending on the political situation. During the reign of different dynasties, it was either an important religious and cultural center or the administrative capital, symbolizing the unity and strength of the Egyptian state. The city was closely associated with the Bastet cults and religious practices that strengthened social ties among the Egyptians, and left a significant legacy in the history and culture of Ancient Egypt.
Archaeological excavations of Bubastis
Bubastis, one of the most important cities of Ancient Egypt, holds many secrets and artifacts that indicate its religious, cultural and political importance. Archaeological excavations in Bubastis began in the nineteenth century, and since then this city has become an important object for the study of ancient Egyptian civilization.
The first excavations in Bubastis were carried out in the middle of the nineteenth century, when European archaeologists began to actively study ancient Egyptian cities. However, the discovery of the city in the twentieth century was of the greatest importance for the study of the city. One of the most important stages was the excavations carried out by French archaeologists under the leadership of Georges Sarton in the 1920s. They uncovered numerous important artifacts that greatly expanded the understanding of the city.
One of the biggest archaeological finds in Bubastis was the remains of the huge Bastet temple, which was the main religious center of the city. Archaeologists discovered columns, walls, and reliefs depicting scenes of religious rituals and festivals in honor of the goddess Bastet. This allowed us to understand not only the architectural features of the temple, but also the role it played in the life of the Egyptians.
Other important architectural finds include the remains of large courtyards, shrines, and other religious buildings, as well as the remains of residential areas and commercial areas. The architecture of Bubastis combined traditional Egyptian elements with new ones, reflecting the development of the city’s culture in different periods of its existence.
Archaeologists have discovered numerous statues, amulets, frescoes, and other religious objects that testify to the importance of Bastet in the religious practice of the Egyptians. One of the most interesting finds was the statues of cats, which were often depicted as sacred animals associated with Bastet cults. Cats were an important symbol of the city, as the goddess Bastet was the protector of cats and was considered the patroness of the household.
In addition to religious objects, archaeologists have also found many household artifacts, such as utensils, tools, and jewelry, which helped to study everyday life in Bubastis
Numerous tombs were discovered on the territory of Bubastis, belonging to different periods of the city’s history. Excavations have revealed tombs of aristocrats, priests, and ordinary citizens. Rich objects were found in these tombs, including jewelry, pottery, sarcophagi, and statues of deities that were used in rituals to ensure eternal life for the dead.
Bubastis excavations play a key role in the study of the religious, cultural and social life of Ancient Egypt. The findings testify to the importance of this city as a religious center that attracted pilgrims from all over the country, as well as to the richness and diversity of cultural influences that characterized Egyptian civilization in its heyday.
Today, archaeological excavations in Bubastis continue, and with each new discovery, scientists gain more knowledge about the history of this majestic city and its role in the history of Ancient Egypt.
Bastet Temple: finds and reconstruction
The Temple of Bastet in Bubastis was one of the most important religious centers of Ancient Egypt, dedicated to the goddess Bastet, who symbolized love, fertility, and protection. The temple became a major center of pilgrimage for the Egyptians, and archaeological excavations on its territory allow us to restore many aspects of its architecture, religious significance and material culture.
- Findings at the Temple of Bastet
Archaeological excavations of the Bastet Temple in Bubastis began in the mid-twentieth century, and many important finds have been made so far. Among them:
Bastet statues: Archaeologists have found numerous statues depicting Bastet in the form of a cat or a woman with a cat’s head, which is the main symbol of this goddess. The statues of various sizes and styles reflect different aspects of Bastet’s cult, ranging from her role as a fertility goddess to her revered status as the patron saint of cats.
Reliefs and murals: Reliefs depicting scenes of religious rituals and festivities dedicated to Bastet have been discovered on the walls of the temple. Such scenes often include rituals, sacrifices, and celebrations that emphasize the importance of the temple as a center of religious life.
Amulets and jewelry: Numerous amulets have been found in the temple and surrounding burials that were used in religious rites. These were small statuettes of Bastet, as well as other symbols that had protective power.
Artifacts of everyday life: Finds such as utensils, tools, and jewelry allow us to recreate the daily life of the time, confirming the importance of the temple for the population of Bubastis and its role as a place of spiritual and cultural exchange.
- Architecture of the Bastet Temple
The Bastet Temple was a large architectural complex that occupied a significant part of the territory of Bubastis. The architecture of the temple included several important elements:
The hypostyle hall: This is a large hall where the statue of the goddess was kept. The hall was surrounded by columns that not only supported the roof but also served to decorate the temple. The columns were often decorated with reliefs depicting scenes from the life of Bastet.
Underground premises: Archaeologists have discovered underground parts of the temple where special religious rituals were held. They contained the remains of ritual objects and the remains of sacrifices.
Sanctuaries and altars: The temple had special places for sacrifices, where gifts to the goddess Bastet were brought. This included not only the traditional sacrifices of food and drink, but also ritual dancing and singing.
The portico and courtyard: Architecturally, the temple had an open courtyard where public religious events were held. A portico with columns led to the inner sanctuary, which was the most sacred place in the temple.
- Reconstruction of the temple
The reconstruction of the Bastet temple, based on archaeological findings, is a challenging task for scientists and architects. Since the temple is partially destroyed, most of the information about its architecture and structure can only be obtained through detailed excavations and comparisons with other Egyptian temples.
The reconstruction includes:
Restoration of the structure and details: The found parts of the colonnade, walls with reliefs, and the remains of statues allow scientists to reconstruct the overall appearance of the temple. Some parts of the temple have been restored in modern architectural programs to help visualize its original appearance.
Digitization and virtual reconstructions: Thanks to modern technology, archaeologists have created 3D models of the Bastet temple, which allow them to study the architectural features and structure of the complex without the need for additional excavations.
- The importance of the temple for modern science
The Bastet Temple in Bubastis is a key source of information for studying the religious life of Ancient Egypt. Findings in the temple allow researchers to study not only religious practices and cults, but also everyday aspects of Egyptian life, their artistic traditions, economic ties, and social structure.
Archaeological research and reconstruction of the Bastet temple provide a unique opportunity to restore a part of the religious and cultural heritage of Ancient Egypt, which continues to influence the science and culture of the modern world.
Bubastis’ legacy in the modern world
Bubastis, one of the largest and most important cities of Ancient Egypt, has left a vast legacy that continues to influence culture, science, and tourism in the modern world. Its religious, cultural and architectural heritage plays an important role in understanding ancient Egyptian civilization.
- Religious heritage
One of the main components of Bubastis’s heritage is its religious influence, in particular the cult of Bastet. The goddess Bastet, who was a symbol of hearth, fertility, and protection, continues to capture people’s imagination to this day. Her images, such as statues of cats and images of the goddess with a cat’s head, remain symbols of peace, love and protection. Bubastis was an important pilgrimage site, and festivals in honor of Bastet attracted thousands of people from all over Egypt.
In the modern world, although the religious practices of ancient Egypt are long gone, the cult of Bastet sometimes appears in popular culture, art, and even in religious movements that revive ancient practices.
- Archaeological heritage
Archaeological excavations at Bubastis have uncovered many important finds, including temple remains, statues, reliefs, and other artifacts that tell the story of the religious and daily life of the Egyptians. The Bastet Temple, which was one of the largest religious centers in Egypt, continues to attract the attention of archaeologists and tourists from all over the world. The remains of this majestic structure allow modern researchers to better understand the architecture and religious practices of Ancient Egypt.
The preservation and study of artifacts from Bubastis helps to reveal many aspects of Egyptian culture that have not yet been explored or studied to the fullest extent. For example, the study of household items, jewelry, and amulets gives an idea of the daily life of the city’s inhabitants.
- Cultural heritage and art
The heritage of Bubastis has become a significant source for the development of art and culture. The images of Bastets and cats have become part of popular culture, which is reflected in contemporary works of art, cinema, and literature. The images of Bastet, symbolizing femininity, protection and mercy, are often found in contemporary design and decorative art.
In addition, the architectural elements of Bubastis, such as columns and temples, have become a source of inspiration for architects and artists looking for a connection between ancient Egyptian traditions and modern styles.
- Tourism and heritage promotion
Today, Bubastis is an important destination for tourists and archaeologists. Tourism related to visiting ancient Egyptian cities and temples, including Bubastis, helps preserve the heritage of this city and enables a wider audience to learn about its significance. Egypt’s world heritage attracts millions of tourists every year, and many of them are eager to visit Bubastis to see the remains of temples and learn more about religious life in ancient Egypt.
Also, archaeological sites and museums that house artifacts from Bubastis are important for educating and popularizing Egyptian history among scholars and the general public.
- Studying history and science
Thanks to archaeological excavations and the preservation of material monuments, Bubastis has become a key site for the study of the history, archaeology, religion and art of Ancient Egypt. The study of Bubastis allows modern scholars to better understand not only religious and cultural traditions, but also the political, social and economic organization of Egypt.
The findings made during excavations in Bubastis continue to amaze scientists and provide new information about life in ancient Egypt. The city helps to restore important pages of the history of this ancient civilization and understand how it influenced the modern world.
- Heritage in modern pop culture
Bubastis and the cult of Bastet leave their mark not only in science but also in pop culture. The images of the goddess Bastet, cats, and ancient Egyptian traditions are actively used in modern films, books, and video games. Bastet, as the goddess of hearth, fertility, and protection, continues to be a popular symbol in contemporary art and design.
The heritage of Bubastis, including its religious, architectural, and cultural monuments, is of great importance to the modern world. It helps to keep us connected to the majestic history of Ancient Egypt, supports cultural tourism and scientific research, and inspires new creative ideas in art and pop culture.
Conclusion
As one of the largest and most important cities of Ancient Egypt, Bubastis played an important role in the development of religion, culture and politics of this great civilization. The city was not only a religious center dedicated to the goddess Bastet, but also an important trade and administrative hub that united different social and cultural strata of Egypt. Its temple, shrines, and architectural monuments continue to inspire researchers, historians, and archaeologists, helping to provide a deeper understanding of Egyptian social and religious practices.
The role of Bubastis in Egypt’s religious life was extremely important, as it was the center of huge religious festivals and pilgrimages that brought together thousands of people from all over the country. This city became a symbol of religious unity and cultural diversity, as numerous traditions and cultures intertwined in it.
Archaeological findings, excavations of the Bastet temple, and the study of everyday objects allow us to reconstruct not only the architecture of the city but also to understand the daily life of its inhabitants. The heritage of Bubastis is an important part of the history of Ancient Egypt, and its importance for modern science, culture, and tourism cannot be overestimated. Bubastis has left an indelible mark on the cultural and religious heritage of humanity that continues to influence the modern world.