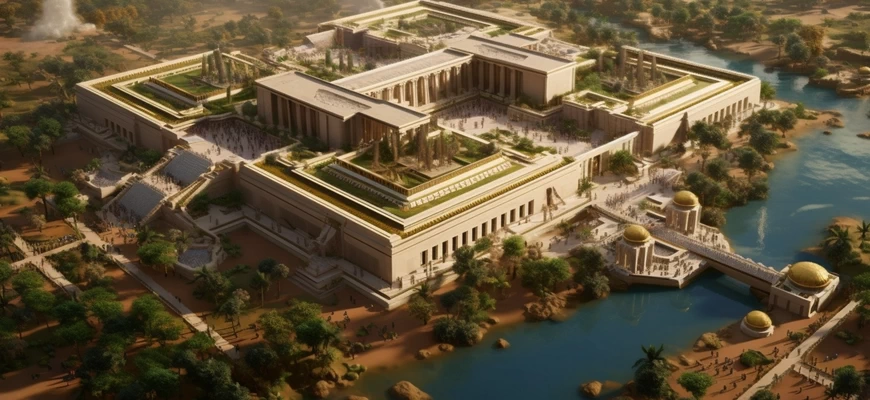
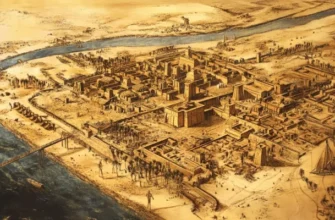
Thebes, once the cultural and political heart of ancient Egypt, fascinates with its mystery and grandeur. Located on the east of the Nile, this city not only served as the capital, but also witnessed many historical events.
The importance of Thebes in Egyptian history
Thebes played a key role in Egyptian history as a political, cultural, and economic center. Founded more than 5,000 years ago, it became the capital and symbol of ancient Egyptian civilization. The main role of Thebes in history included political significance, cultural center, trade hub and religious importance. Due to its wealth, grandeur, and cultural heritage, Thebes remains a key research object for archaeologists and historians, helping to understand the development of ancient Egyptian civilization.
History of Thebes
The history of Thebes dates back more than five thousand years. Founded on the east of the Nile, this ancient city became the cultural, political, and economic center of Egypt. Thebes witnessed the flourishing of various dynasties and pharaohs, and served as a place of development for art, science, and religion. Its importance was manifested not only in political stability but also in the greatness of architectural masterpieces, trade routes, and religious rites. Archaeological excavations reveal the secrets of this majestic city, revealing the multilayered history of its existence.
Founding and development
According to legend, Thebes was founded more than 5 thousand years ago, and it became an important center of ancient Egypt. Legends tell of the pharaohs who laid the first foundation stones, defining the city as the future capital.
With the development, important historical events took place in Thebes. The city became the seat of power of various pharaohs and dynasties, developing as the political center of Egypt. In its heyday, Thebes amazed the world with its architecture, the grandeur of temples and palaces.
Founded on the banks of the Nile, the city also played an important role in trade and economy, providing a link between different regions. Religious practices and rituals performed in the temples contributed to cultural development and supported important aspects of ancient Egyptian life.
Archaeological research continues to reveal the secrets of the city’s foundation and development.
Legends about the foundation
The legend of Menes:
Pharaoh Menes, preferring to unite the regions of Upper and Lower Egypt, chose Thebes as the capital of his united state, establishing it as a symbol of unity.
The legend of Menes is reflected in the mythology of ancient Egypt and is associated with the founding of the city of Thebes. According to this legend, Menes (sometimes known as Narmer), a pharaoh of the Early Ancient Egyptian era, decided to unite the divided regions of Upper and Lower Egypt.
Menes chose Thebes as the centerpiece of his unified state, establishing the city as the new capital. This decisive decision determined the future role of Thebes in the country’s history and laid the foundation for the idea of unity and integrity of the Egyptian people. The legend of Menes emphasizes the importance of the city as a symbol of unity and stability in ancient Egypt.
The legend of the appearance of the god Ra:
According to beliefs, the sun god Ra chose Thebes for his first earthly appearance, making the city a special and sacred place.
The legend of the appearance of the god Ra is reflected in the mythology of ancient Egypt and gives the city a special divine status. According to this legend, the sun god Ra, who is one of the most important gods in the Egyptian pantheon, chose Thebes for his first earthly appearance.
This legend says that the god Ra, like the sun, appeared at dawn in Thebes. His appearance testified to the city’s special definition, endowed with divine blessing. This placement of Thebes under the protection of the god Ra emphasizes his sacred status and importance in the cosmological order of ancient Egyptian religion.
The legend of the foundation of the goddess Isis:
According to one legend, the goddess Isis, dressed in black clothes, arrived in Thebes after the murder of her husband Osiris. Her dubious adventure established the city as a shrine to the patron saint of family and motherhood.
The founding legend associated with the goddess Isis is striking in its power and emotional depth in the context of the ancient Egyptian city of Thebes.
Her grief and devotion to her late husband influenced Thebes, making it a shrine to the patron saint of family and motherhood.
This legend emphasizes the deep religious and emotional aspects of Thebes. The city becomes a witness and participant in a great religious and mythological story, where divine events and human feelings are intertwined, giving the city not only historical significance but also a deeper religious meaning.
These legends add depth to the story, reflecting the various aspects of its origin and its particularity in the culture and religion of ancient Egypt.
Development of the city during different eras
The development of the city of Thebes during different epochs in Egyptian history was extremely multifaceted and determined by various historical and cultural influences. Here is an overview of the key stages of the city’s development:
Ancient Egyptian Era:
Thebes became the capital and cultural center of early ancient Egyptian states, building majestic palaces and temples.
Ancient Egyptian period:
The city continued to play a key role in the stability and development of the country under various pharaohs and dynasties.
The Hyksos Era:
The conquest of Egypt by the Achaemenid Persians and the subsequent influence of Greek and Roman cultures brought new architectural styles and elements to Thebes.
Byzantine and Arab periods:
Under Byzantine rule and then Arab influence, Thebes underwent changes in architecture and cultural heritage.
Ottoman Era:
Ottoman rule brought its own characteristics to the development of the city, including new buildings and infrastructure.
Modern times:
Today, Thebes remains an archaeological and historical attraction, famous for its role in ancient Egyptian history, as well as an important tourist destination.
Role in Ancient Egyptian Society
Thebes played a crucial role in ancient Egyptian society as a political, cultural and religious center. Its role can be viewed in different aspects:
Political significance:
Thebes was the capital of various dynasties and pharaohs, making it the political heart of ancient Egypt. The palaces and residences of the rulers were located here.
Cultural Center:
The city was a center of art, science, and literature. Majestic temples, palaces and other architectural masterpieces testify to the cultural wealth of Thebes.
Religious Importance:
Thebes was of great religious importance. It was home to temples for various gods and goddesses, including the main god Amun.
Economic Role:
Located on the east of the Nile, Thebes was an important trade hub, contributing to the development of trade and the economy.
Center of Education and Science:
Thebes was home to major educational institutions where scholars and priests studied astronomy, mathematics, medicine, and other sciences.
The role of Thebes in ancient Egyptian society was so decisive that it influenced a huge part of the country’s life, giving the city a special status and historical significance.
Architecture and Monuments
The architecture and monuments of Thebes testify to the majesty and cultural flourishing of the ancient Egyptian city. Here are some of the most notable architectural elements and monuments:
Temple of Amun-Ra:
The largest and most important temple in Thebes, dedicated to the god Amun and the sun, the god Ra. It consists of massive walls, courtyards and shrines.
Temple of Osiris:
This temple was dedicated to the god Osiris, an important deity in ancient Egyptian mythology. It is known for its huge statue of Osiris.
Pharaoh’s Palace:
The residence of the pharaoh, a huge building that reflected the power and wealth of the city.
Obelisks of Thebes:
Obelisks, tall stone stelae with carved hieroglyphics and illustrations that indicated religious or historical events.
Thebes Medical School:
A center for the study of medicine and science where physicians and scientists learned healing and medical practices.
Western Temple:
A temple complex in the west of Thebes that served as a place for religious rites and celebrations.
These monuments are striking in their grandeur and architectural craftsmanship, testifying to the greatness of ancient Egyptian civilization and the role of Thebes in its history.
Archaeological excavations
Archaeological excavations in Thebes are a key element in uncovering and understanding ancient Egyptian history and culture. These excavations make a great contribution to our knowledge of the development of the city and ancient Egyptian society in general. The main aspects of archaeological research in the city include:
Excavations of temples and shrines:
The uncovering of temples dedicated to various gods and goddesses allows us to study religious practices and the role of these shrines in ancient Egyptian cultural life.
Exploring the Palace of the Pharaoh:
The excavation of the pharaoh’s residence helps to reveal the personal life and rule of the pharaohs, as well as an understanding of the architecture and location of important structures.
Reconstruction of Life and Economy:
Finds in excavations, such as domestic objects and economic structures, allow archaeologists to reconstruct the daily life and economy of an ancient city.
Study of Architectural Structures:
The study of buildings and infrastructure reveals the architectural achievements and technologies used in ancient Thebes.
Uncovering Artistic and Archaeological Finds:
Finds of artistic and archaeological objects, such as sculptures, jewelry, and pottery, reveal details of artistic and craft activities.
Archaeological excavations in the city continue to make an important contribution to our historical and cultural heritage, helping to restore and understand the ancient city and its role in ancient Egyptian society.
Conclusion
Thebes, the capital of ancient Egypt, remains a key site of study for archaeologists and historians. Located on the east of the Nile, this city is steeped in the grandeur of history, culture, and religion. Excavations reveal its role as a political, cultural, and religious center where art, science, and economy developed.
Historical significance: Thebes was founded over 5,000 years ago and played a key role in the development of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Religious Importance: The temples of Thebes were dedicated to important deities, reflecting religious belief and rituals.
Architectural Treasures: The majestic temples, palaces and obelisks testify to a high level of architectural skill.
Trade Hub: Its location on the east of the Nile made Thebes an important trade hub, contributing to economic development.
Archaeological Research: Excavations are helping to restore the history and reveal the secrets of this ancient city.
Thebes remains an inexhaustible source of knowledge for those interested in ancient history and culture. Further study of archaeological discoveries, revealing religious and cultural aspects, as well as understanding the influence of Thebes on the formation of modern Egypt.