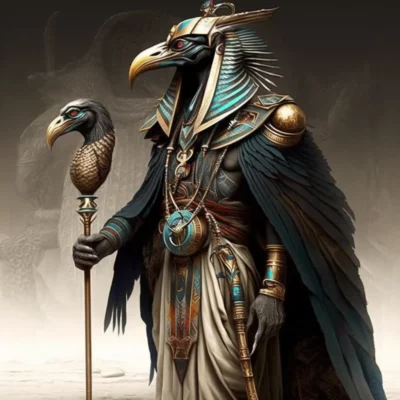
Osiris is one of the most famous gods of Egyptian mythology, and his name is associated with the word “asar”, which means “bound to the earth”. Osiris was the god of the underworld, life and resurrection, and his cult played an important role in the religious life of ancient Egypt.
According to legend, Osiris was one of the sons of the heavenly god Geb and the goddess Nut. He became the ruler of all people, taught them how to farm and gave them knowledge about the gods. However, his brother Seth felt jealous of Osiris and decided to kill him. He insidiously stole his body, dismembered it into several parts, and scattered it all over the country.
After Isis, the wife of Osiris, found all his parts, she was able to restore his body with the help of magical knowledge and resurrect him. Osiris became the god of the underworld and the deity of life and resurrection, and his resurrection symbolized rebirth, the beginning of a new life, and the rebirth of nature.
Osiris also played an important role in the mythology of the Sun and its path across the sky. According to legend, Osiris was the first god to descend from heaven to earth, so he was associated with the earth and its fertility. His death and resurrection symbolized the cyclical process of nature, which repeats every year.
The cult of Osiris was of great importance in ancient Egyptian religion and art. His images can be found on various objects such as temple walls, sarcophagi, amulets, and other religious objects. Also, the name of Osiris was contained in many proverbs, sayings and riddles of the ancient Egyptian language.
The entire cult of Osiris reflected various aspects of life and nature, such as birth, life, death, and rebirth. He also played an important role in the beliefs about life after death, which for the Egyptians was a new stage of existence.
In today’s world, the image of Osiris remains one of the most famous symbols of Egyptian culture, and his legends and myths continue to inspire artists and writers from around the world. His significance as the god of life and resurrection continues to influence our understanding of nature and its cyclical processes.
- Characteristics of Osiris
- Description of the appearance and character of the god Osiris
- Interaction of Osiris with other gods and goddesses
- Symbolism of Osiris
- Legends and myths
- Description of the legend of the creation of the world, in which Osiris participates
- The legend of Osiris’ murder by his brother Seth and rebirth
- The role of Osiris in the mythology of the Sun and its path across the sky
- The cult of Osiris
- Description of religious rites and celebrations associated with Osiris
- Description of the temples dedicated to Osiris and their significance
- The religious position of Osiris in ancient Egyptian society
- Influence on art and culture
- Description of images of Osiris in Egyptian art
- The role of Osiris in the culture of ancient Egypt and his legacy
- Conclusions.
Characteristics of Osiris
Description of the appearance and character of the god Osiris
Osiris was depicted as a green-colored deity with a white or golden shell, symbolizing rebirth. He was also supposed to be tall, with the footprints of ancient Egyptian kings.
His character was considered to be kind and merciful, and he was the patron saint of all living beings. Osiris was considered the god of wisdom, knowledge and magic, and was also the patron saint of agriculture and agricultural technology.
His role as the god of life and death and the god of rebirth emphasized his kind and merciful nature. Osiris was sensitive to the suffering of his worshippers and protected them from evil spirits.
In the society that believed in Osiris, wisdom and mercy were valued, and it was believed that these traits were important for achieving grace and happiness in the afterlife.
Interaction of Osiris with other gods and goddesses
Osiris interacted with many other gods and goddesses of Egyptian mythology. He was the brother and husband of Isis, who was the goddess of motherhood, protection, and magic, and the father of Horus, the god of the sky.
Osiris was also associated with other important gods, such as Ra, the sun god, Anubis, the god of mummification, and Thoth, the god of wisdom and writing. In mythology, Osiris was killed by his brother Seth, who symbolized power and evil, but was later revived with the help of his wife Isis.
Osiris has also been associated with the idea of judgment and rebirth, as he was a judge after death, and is believed to have received the souls of the dead into his realm after they had been judged and tested in the “scales of truth.” His name was also associated with the word “silver,” symbolizing wealth and rebirth, and it is believed that he granted his worshippers blessings for material success.
All of these relationships helped Osiris embody important concepts such as rebirth, wisdom, mercy, and judgment. His role in Egyptian mythology was very large and he performed many different functions that played an important role in the life of the ancient Egyptian people.
Symbolism of Osiris
Osiris had many symbols that reflected different aspects of his character and functions in Egyptian mythology. Some of his symbols include:
The rod or caduceus – a symbol of power and control over life and death. This symbol is also associated with the realm of magic and wisdom.
A headdress with two feathers is a symbol of justice and fairness. It is also associated with the ability of Osiris to rebirth and rebirth.
White clothes are a symbol of purity and impeccability, which are key attributes of Osiris as the god of the afterlife.
The pharaoh’s mace is a symbol of power and rule, which is also associated with the divine aspects of Osiris.
The water droplet is a symbol of reproduction and vitality, which is also associated with the god Osiris because of his ability to be reborn and reborn.
Each symbol of Osiris had its own meaning, but they all reflected key aspects of his character and role in Egyptian mythology.
Legends and myths
Description of the legend of the creation of the world, in which Osiris participates
In Egyptian mythology, there are several legends about the creation of the world, one of which involves Osiris. According to this legend, at the beginning of time there was a wasteland called Nun. From it emerged the Nile River, which brought life to the earth. The first people appeared on the banks of the river.
One day, Osiris, who was the god of the afterlife, took on the challenge of the god Set, the god of chaos and destructive forces. In the battle between them, Osiris won, but Seth later conspired with the goddess Nephthys and instead of keeping his word and giving power to Osiris, he killed him and divided his body into 14 parts.
His wife Isis found all the parts of his body and restored his life. Osiris then became the god of the underworld and even became its judge. This legend of Osiris reflects his role as the god of the afterlife and rebirth, as well as the loyalty and devotion of his wife Isis.
The legend of Osiris’ murder by his brother Seth and rebirth
In Egyptian mythology, there is a legend about how Osiris was killed by his brother Seth. According to this legend, Seth was jealous of his brother Osiris for his power and popularity among people. One day, Seth challenged Osiris to a fight, and during the fight, he killed him and divided his body into 14 parts.
Isis, the wife of Osiris, after finding all the parts of his body, put them back together to revive him. Using a magic formula she received from the gods, she restored Osiris’ body. However, Osiris could not return to the world of the living and was forced to live in the world of the dead.
This legend about the killing of Osiris and his rebirth reflects the Egyptians’ belief in the afterlife and the restoration of vital energy after death. It also shows that Osiris was the god of life, death, and rebirth, and his wife Isis was the goddess of motherhood, fidelity, and magic.
The role of Osiris in the mythology of the Sun and its path across the sky
In Egyptian mythology, Osiris also plays an important role in myths related to the Sun and its path across the sky. It was believed that every day the sun god Ra had to pass through the world of the dead to return to the world of the living the next day. According to legend, Osiris was the lord of the world of the dead, so Ra turned to him to get help during his journey.
Osiris helped Ra pass through the world of the dead, where he was exposed to various dangers and trials. At the same time, Osiris symbolized rebirth, so this legend shows how the Sun “dies” every day in the world of the dead and then “reborn” the next day, just like Osiris.
In addition, Osiris was also considered the god of agriculture, and the springtime was considered his rebirth and was associated with new sowing and the beginning of agricultural work. Thus, Osiris was a symbol of rebirth, life, and fertility, and his role in the sun myths emphasized his great importance in Egyptian mythology.
The cult of Osiris
The cult of Osiris in Egypt was one of the most widespread and important cults of the ancient world. The god Osiris was the patron saint of agriculture, fertility, the underworld, and the afterlife.
Every year in Egypt, celebrations were held in honor of Osiris, which were associated with his legends and myths. One of the most famous festivals was the Haith Festival, which took place in the city of Abydos in the middle of summer. During this festival, rituals related to the death and rebirth of Osiris were performed, as well as other rituals designed to attract fertility and prosperity.
Osiris also had his own temples located in different cities of Egypt. One of the most famous temples was in the city of Abydos, where he was buried. The temple of Osiris in Abydos was a place of pilgrimage for Egyptian priests and ordinary people.
In the cult of Osiris, there were also various rituals associated with death and rebirth. For example, it was believed that the solemn burial rite was to help the soul of the deceased to be reborn in the afterlife, where it would become one of the people of Osiris.
The belief in Osiris continued to exist for many centuries after the end of the civilization of ancient Egypt. The ideas of rebirth and the afterlife associated with this god influenced the formation of religious views in different cultures and eras.
The Egyptian god Osiris was one of the most important gods in Egyptian mythology, and his cult was very common in the religious practice of ancient Egypt. Osiris was the god of death, rebirth, and fertility, and these aspects of him were reflected in various aspects of the cult.
One of the most important places of the Osiris cult was the tomb of the god in Abydos, where rites of rebirth and worship were performed. Osiris was also often depicted on various amulets and talismans that were supposed to protect against evil spirits and bring good luck. Osiris was also often depicted as a mummy, as he was associated with death and rebirth.
Celebrations associated with Osiris were usually linked to the cycle of agricultural work. One of the most important rituals associated with Osiris was the Osiris festivals, which were celebrated every year on the summer solstice. This holiday symbolized the transition from hot summer to cool autumn, when agricultural work began with sowing and harvesting.
Osiris was also associated with religious and mystical rites related to death and rebirth. For example, it was believed that deceased souls were transformed into Osiris and reborn in the afterlife.
Initially, after the advent of Christianity, the cult of Osiris disappeared, but over time, some aspects of it were revived in folk rituals. Today, the cult of Osiris is not widespread, but it has its adherents in different parts of the world. His image is depicted on many amulets and talismans that believers carry with them to protect them from evil forces.
There are also various modern organizations that practice different forms of Osiris worship, such as Pagan cultures and necromantic associations. The cult of Osiris is also popular among some magicians and occultists who use his symbolism and energy in their practices.
In high antiquity, the cult of Osiris was one of the most widespread and important in Egypt. He symbolized death and rebirth, fertility and power over the afterlife. Today, the cult of Osiris may not be as widespread, but its legends and symbolism continue to be a source of interest and study for many people interested in mythology and spirituality.
Description of religious rites and celebrations associated with Osiris
In Egyptian religion, Osiris played an important role and many religious rites and celebrations were dedicated to him. One of the most famous rituals associated with Osiris is the “Osirion”, a festival that took place in honor of the god in the city of Abydos. Many cities also held celebrations in honor of Osiris, including the city of Busiris, where the Great Circumnavigation festival took place, during which a statue of the god was carried on boats.
One of the most important rituals was the rebirth of Osiris, symbolized by the explosion of the solar disk at dawn. This rite was called the “Heliopolitan resurrection ritual”. It was also known that Osiris had power over life and death, so he was often depicted together with other deities who symbolized this life cycle.
Other rites are associated with funeral rituals and ancestor worship. In the religion of Osiris, it is believed that he was the first king, and therefore he had a special significance in funeral rituals. For example, during the burial of a pharaoh, his mummy was depicted as Osiris.
In general, Osiris was considered one of the most revered gods in Egyptian religion, and his influence on Egyptian culture and art remained noticeable for many centuries.
Description of the temples dedicated to Osiris and their significance
Osiris is one of the most important deities of ancient Egypt and was honored by a large number of temples throughout the country. Temples dedicated to Osiris were of great importance to ancient Egyptian religion and culture.
One of the most famous temples dedicated to Osiris is located in Abydos. The temple was founded in the Second Dynasty (around 2890-2686 BC) and was expanded over the centuries. It had great religious and cultural significance for the Egyptian people and was a place of pilgrimage for thousands of believers.
The Temple of Osiris in Abydos was a place where rituals and commemorative events were held in honor of the god. Chapels were built in the temple, where holy relics and images of Osiris were kept. In addition, rituals related to the death and resurrection of Osiris, who, according to legend, was revived after his death, were held in the temple.
Another famous temple dedicated to Osiris is located in Abu Simbel. This temple was founded by Pharaoh Ramses II (circa 1279-1213 BC) and is known for its huge statues of Ramses and Osiris.
In many other places throughout Egypt, temples dedicated to Osiris were also built, which played an important role in the culture and religion of ancient Egypt. They served not only as a place of worship, but also as a place to store sacred objects and relics that were considered extremely important to the Egyptian religion.
The significance of the temples dedicated to Osiris was that they served as a place for people to communicate with the deity, and also maintained a link between the living and the dead. For the ancient Egyptians, the belief in life after death and the resurrection of the god Osiris was very important, so the temples of Osiris were important as a symbol of eternal life and resurrection.
The temples of Osiris also played an important role in state and social events. They were the venue for celebrations and ceremonies related to the coronation of pharaohs and other important events in the life of the country. Thus, the temples of Osiris became the center of not only religious but also cultural life in ancient Egypt.
In the modern era, some of the temples of Osiris are being restored and restored to preserve the cultural heritage of ancient Egypt. The temples of Osiris remain popular tourist attractions that attract thousands of visitors from all over the world.
The religious position of Osiris in ancient Egyptian society
Osiris was one of the most revered deities in the ancient Egyptian pantheon. His religious position was very high, as he acted as a deity associated with death, resurrection and eternal life.
In ancient Egyptian mythology, Osiris was recognized as the deity of life after death, who was supposed to control the rebirth of the souls of the dead in the Life of the Other World. He was also associated with the earth, agriculture, and prosperity, as his death and resurrection symbolized the cycle of nature, from birth to death and rebirth.
Osiris also acted as the patron saint of justice, as he himself was a judge amid the myth of his killing and rebirth. He represented the ideals of ancient Egyptian culture, such as spirituality, morality, justice, and kindness.
Thus, Osiris was the central deity of the ancient Egyptian religion, which had a great influence on the cultural, social and religious aspects of the ancient Egyptian society. His cult and worship have survived for thousands of years, and he remains an important symbol for modern Egyptians and people around the world who study ancient Egyptian culture and history.
Influence on art and culture
Osiris is a deity of ancient Egyptian mythology, and as such, he had a significant impact on the art and culture of ancient Egypt. Osiris was the god of fertility, agriculture, religious theology, and life after death. He was also associated with grain, which was the main cultural component in ancient Egyptian society.
In the art of ancient Egypt, Osiris was often depicted as a man with a green face, symbolizing growing grain. He could also be depicted with a scepter and a bull’s head, indicating his roles as ruler of the earth and god of fertility.
Osiris was also one of the main gods associated with life after death. He was probably the first god to be associated with the idea of resurrection and eternal life. This belief in eternal life after death was a major aspect of ancient Egyptian religion and culture, and it had a significant impact on the art and architecture of ancient Egypt.
In many temples and pyramids, buildings associated with the cult of Osiris, you can see images of the god and his story. These images inspired other artists to create new works of art that reflected cult ideas and beliefs about life after death.
Thus, Osiris, as a god of ancient Egyptian mythology, had a significant impact on the art and culture of the time.
Osiris occupied an important place in the ancient Egyptian religion, which had a significant impact on the life and culture of the time. The god Osiris was known for his wisdom and knowledge, and this influenced the views of ancient Egyptian philosophers and scientists.
The importance of Osiris for the ancient Egyptian culture can be felt in other aspects as well. For example, he was associated with the concept of truth, which was of great importance for ancient Egyptian morality and ethics. This is probably why the deity became an important element in religious rituals related to the judgment of the dead and the eternity of souls.
In the modern world, depictions of Osiris and his story can still be found in various cultures that take inspiration from ancient Egyptian mythology. This can be found in various art forms, for example, from architecture to painting and sculpture. Thus, Osiris and his cult have a significant influence on the culture and art of not only ancient Egypt, but also the modern world.
Description of images of Osiris in Egyptian art
Osiris is one of the most famous and widespread gods in ancient Egyptian mythology. Depictions of this god can be found in various forms of art, from painting and sculpture to paintings on the walls of temples and tombs.
Osiris was usually depicted as a man with a green face, symbolizing his power over nature. He had a long beard and hair, which was often twined with a snake. He usually held symbols of power, such as a rod and a whip.
One of the most famous images of Osiris is his image as a mummy. He was usually depicted in the chest area, where he had his famous symbol – the symbol “Ankh”, which means life. This symbol reminded us that Osiris was the god of eternity and rebirth.
Another famous image of Osiris is his ship. According to legend, Osiris was sailing on a ship through the heavenly waters, accompanied by other deities and his sister-wife Isis. This image was often found on the walls of temples and tombs.
However, images of Osiris could vary depending on the time and place of creation. For example, in the late period of ancient Egyptian history, Osiris was depicted as the main god, burdened with modern clothes and jewelry. Also, different regions of Egypt could have their own variations of Osiris images.
The role of Osiris in the culture of ancient Egypt and his legacy
Osiris was one of the most important gods in ancient Egyptian mythology and culture. He was the god of death, rebirth, and power, and the county of his cult was very widespread in Egypt.
Osiris was considered the patron saint of farming and agriculture, and was also the god of judgment and power. Ideas about him were important to the ancient Egyptian view of life and death, and his cult was associated with religious rites that accompanied burials, helping the souls of the dead to transform into deities.
Osiris was also associated with the myth of the struggle between good and evil, in which he was treacherously killed by his brother Seth, but later revived thanks to the help of his sister-wife Isis. This myth of rebirth and resurrection played an important role in religious rites and rituals related to the dead and their transition to the world of the dead.
The legacy of Osiris is reflected in many aspects of ancient Egyptian culture. His cult persisted in Egypt for thousands of years and had a great influence on the development of ancient Egyptian art, architecture, literature, and philosophy. The myth of Osiris and his revival played an important role in shaping the ancient Egyptian idea of eternal life and the afterlife.
The legacy of Osiris has survived to this day. Many cultures and religions around the world still use and interpret his myths, rituals, and symbolism. There are also various variations of the myths about Osiris in different cultures that were influenced by ancient Egyptian mythology.
The myth of Osiris also became the basis for various literary works written in Egypt in different historical eras. For example, the great work of ancient Egyptian literature, The Book of the Dead, includes many rituals and ceremonies associated with the rebirth of the dead and the hope of eternal life, which are based on the myth of Osiris.
In art, Osiris was depicted as the god of greenery, grain, and fertility, often depicted sitting or standing, with a tall, multi-layered crown that symbolizes power. Osiris can also be depicted holding a staff, which is a symbol of power and authority.
Conclusions.
The general characterization of the role of Osiris in Egyptian mythology and religion shows that he was one of the most important gods of the ancient Egyptian pantheon. He was the god of fertility and harvest, the god of the dead and rebirth, and a symbol of judgment and justice. His myth of death, rebirth, and triumph over evil became the basis for various religious rites and rituals associated with the hope of eternal life.
Osiris’ influence on the culture and art of ancient Egypt was significant. His image appears on many different publications and art objects, including statues, pyramid walls, papyri, images on temple walls, etc. In addition, the myth of Osiris became the basis for various literary works, such as the Book of the Dead.
It is difficult to overestimate the importance of Osiris in ancient Egyptian culture. He was a symbol of hope for eternal life, fertility, justice and fairness, and his myth of death and rebirth played a significant role in shaping the religion and worldview of ancient Egypt. Therefore, Osiris continues to be an important symbol not only for modern Egyptians, but also for people around the world who are interested in ancient culture and history.